5 Lesser-Known Benefits of Industrial Machine Vision
Industrial machine vision is widely recognized for improving inspection accuracy, production speed, and quality control. These primary benefits are well understood and often form the basis for adoption decisions. However, once machine vision systems are deployed at scale, industrial end-users often begin to realize secondary advantages that were not part of the original plan.
These lesser-known benefits do not replace the core value of machine vision — they compound it. Below are five operational advantages that are frequently overlooked but increasingly important in modern industrial environments.
1. Enhance Workplace Safety with Machine Vision
Machine vision can act as an automated visual compliance monitoring system in environments where safety relies on consistent human behavior. Vision systems continuously validate safety conditions in real time, rather than depending solely on periodic audits or manual supervision.
AI-based vision can detect missing personal protective equipment (PPE), unsafe reach-in behavior near active machinery, or unauthorized presence in restricted zones. These detections trigger alerts or automated system responses before an incident occurs.
This benefit is often overlooked because machine vision initiatives are typically led by quality or operations teams rather than safety departments. In practice, safety improvements emerge as a direct result of continuous visual validation, reducing incidents, stoppages, and improving accountability across shifts.
Machine vision systems enable continuous safety monitoring without disrupting operations
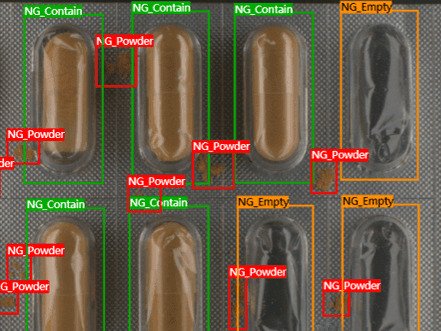
2. Achieve Consistent Product Quality Across Production Lines
Most discussions around machine vision focus on its ability to detect defects. Less attention is given to its role in delivering repeatable and uniform quality judgments across time, operators, and production sites.
Manual inspection is inherently variable. Even well-trained operators apply standards slightly differently, depending on factors such as fatigue, experience, or workload. Machine vision eliminates this variability through consistent application of inspection criteria, improving first-pass yield and reducing false rejects.
This consistency becomes especially valuable in multi-shift operations, high-mix production, or distributed manufacturing environments. The result is fewer defects, more predictable quality outcomes, and minimized rework.
Machine vision applies consistent inspection criteria, detecting subtle quality deviations in real time
3. Detect Process Drift Early to Prevent Defects
Machine vision extends beyond pass/fail inspection by providing process anomaly detection. Continuous analysis of visual characteristics such as alignment, spacing, surface texture, or geometry allows vision systems to identify subtle deviations that precede defects.
These deviations often indicate upstream issues such as tool wear, fixture movement, or material variation. Early detection allows teams to intervene before defects accumulate or failures occur, stabilizing production processes over time.
This capability is frequently overlooked because traditional vision systems are configured statically and focus on end-of-line inspection. AI-driven machine vision enables trend-based analysis that proactively maintains process stability.
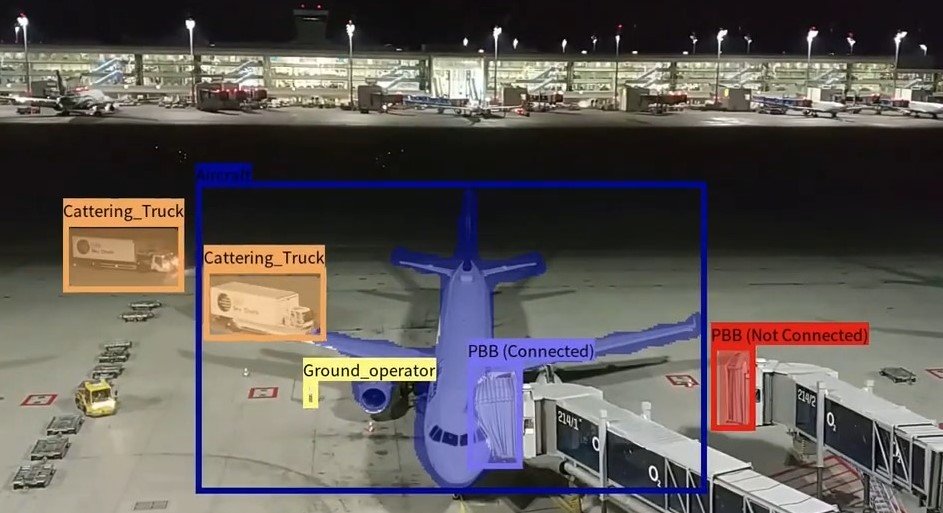
4. Gain Remote Production Monitoring and Process Insights
Machine vision provides more than remote monitoring; it delivers decision-grade visibility into production processes. Visual inspection data, images, and performance metrics can be accessed remotely, allowing engineers and managers to evaluate conditions without being physically present on the shop floor.
This capability supports faster troubleshooting, remote audits, and more effective collaboration between sites. It also reduces reliance on on-site specialists, which is increasingly important in labor-constrained environments.
Remote monitoring is often underestimated because it is framed as a convenience feature. In practice, it becomes a tool for faster decision-making, reduced downtime, and more resilient operations.
Machine vision provides real-time remote visibility into processes, equipment, and asset status
5. Reduce Material Waste and Support Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability initiatives often focus on reporting and measurement after waste has already occurred. Machine vision contributes earlier in the process through the prevention of material scrap and rework.
Early detection of defects prevents defective products from progressing further down the production line, reducing energy consumption and resource use. This proactive approach supports environmental objectives while improving operational efficiency.
This benefit is often overlooked because sustainability impacts are indirect and accumulate over time. In practice, improved first-pass yield, reduced rework, and stabilized processes contribute meaningfully to both environmental and operational goals.
Conclusion
The primary benefits of machine vision — speed, accuracy, and automation — represent only the starting point. Once deployed, machine vision systems begin to deliver broader operational value through improved safety compliance, quality consistency, early process anomaly detection, remote monitoring, and waste prevention.
These advantages are particularly relevant for manufacturers operating in high-mix, labor-constrained, or distributed environments. AI-based machine vision continues to expand its role from an inspection tool to a foundational system for operational control and continuous improvement.
Machine Vision FAQs
What makes modern machine vision different from traditional vision systems?
Modern machine vision uses AI models that adapt to variation in products, lighting, and environments. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, AI-driven vision can handle complex, high-mix scenarios without constant reconfiguration.
Can machine vision reduce false rejects in quality control?
Yes. AI-based machine vision is particularly effective at reducing false rejects by learning acceptable variation rather than relying on rigid thresholds. This improves yield without compromising quality standards.
How does machine vision support predictive maintenance?
Machine vision detects visual indicators of wear, misalignment, or deformation that precede equipment failure. These insights enable maintenance teams to intervene earlier and avoid unplanned downtime.
When does machine vision struggle or fail?
Machine vision performance can degrade when lighting is unstable, training data is insufficient, or processes change without model updates. Successful deployments account for these factors during system design and validation.
Is machine vision suitable for high-mix or low-volume production?
Yes. AI-based machine vision is particularly effective at reducing false rejects by learning acceptable variation rather than relying on rigid thresholds. This improves yield without compromising quality standards.
What should manufacturers evaluate before deploying machine vision?
Key considerations include inspection objectives, environmental conditions, data availability, system integration requirements, and long-term scalability. Evaluating these factors early significantly improves deployment outcomes.