What is Deep Learning?
Introduction to Deep Learning
How Does Deep Learning Work?
Let’s take the example of a child learning to recognize birds in images. The parent first points to the bird in the picture and makes the correct sound. The child then tries to mimic the sound, which is corrected by the parent until the child understands the word. This learning process is similar to how artificial neural networks operate.
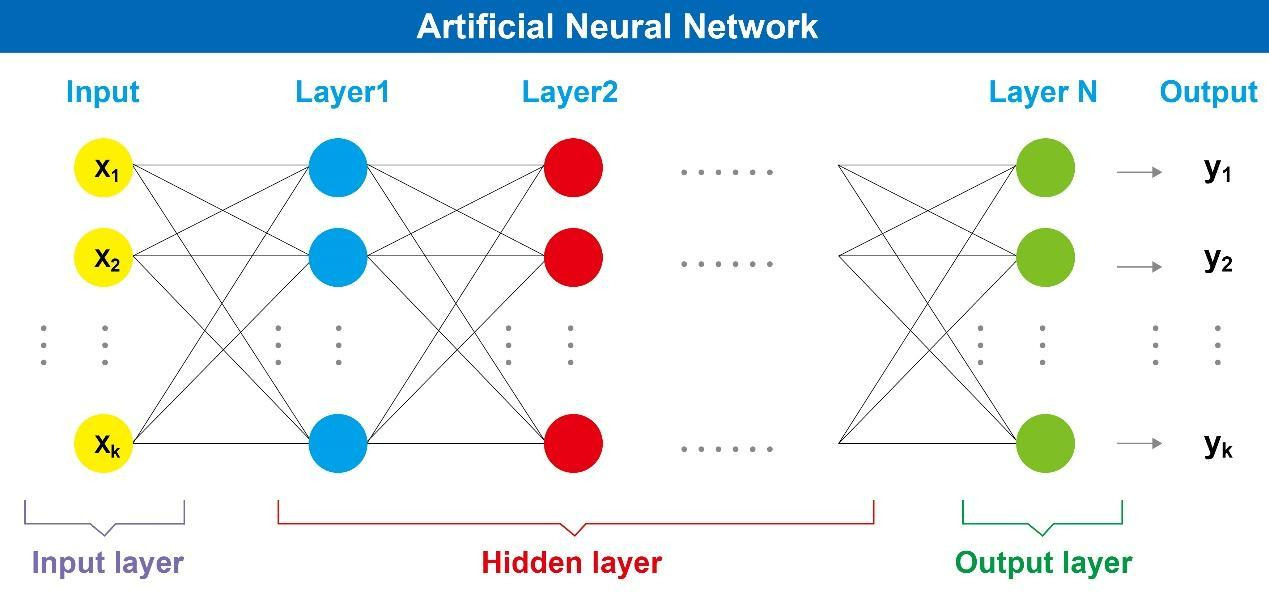
An artificial neural network consists of several layers, including the input layer, the hidden layer, and the output layer, each with its own weights and variables. The nodes in each layer analyze different features of the image. For example, the lowest layer analyzes the contrast of black and white pixels, while the second layer distinguishes lines based on the data from the first layer. By computing non-linear functions across multiple layers, the output layer produces the final value, which is the image’s classification and recognition.
Since these types of neural networks require multiple layers of neurons for data processing, they need to be compared layer by layer to operate, which makes the computational complexity relatively high. This is why deep learning is associated with the concept of ‘depth’.
Why is Deep Learning Important?
What are the Applications of Deep Learning?
Speech Recognition
The main purpose of speech recognition is to enable computers to understand human speech and automatically convert it into text, followed by executing tasks based on the speech signal. Common applications of speech recognition include speech document retrieval, data entry, speech navigation, and indoor device control (controlling the temperature of a thermostat, turning on/off lights, managing home security systems, etc.).
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that helps computers understand and interpret human language. NLP applications are already deeply embedded in our daily lives. For example, virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri and Amazon’s Alexa recognize user commands through speech recognition and provide corresponding responses based on the conversation information, enabling users to effectively manage personal affairs. As IoT devices become more widespread, intelligent assistants are being used in the workplace for tasks like recording conferences and providing automated customer service through chatbots.
Image Recognition
The main purpose of image recognition is to allow computers to extract information from images and videos, enabling them to understand the data through deep learning and to assist humans in making data judgments. Image recognition is a growing area in deep learning, with various applications such as product defect detection, medical imaging, facial recognition, and license plate recognition.
Benefits of Deep Learning for Industrial End Users
Enhanced Quality Control
Predictive Maintenance
Improved Production Efficiency
Advanced Robotics Integration
Real-Time Decision Making
Improved Worker Safety
Deep Learning Summary