What is Machine Vision? Definition, Applications, and Trends
Introduction to Machine Vision
Machine Vision Definition
Difference Between Machine Vision and Computer Vision

Machine Vision
Machine vision is specifically designed for industrial applications, such as manufacturing and quality control. It combines specialized hardware and software to capture, process, and analyze images for automated inspection and decision-making. These systems are optimized for speed, accuracy, and reliability in industrial environments, focusing on predefined tasks.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is a broader field that develops algorithms and techniques to enable computers to interpret and analyze visual data, similar to human perception. Its applications extend beyond industry to fields like robotics, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and medical imaging. Machine vision is a subset of computer vision, tailored for industrial automation and inspection.
Components of Machine Vision Systems
The host computer acts as the central processing unit, managing data and system functions.
The frame grabber captures image data from the camera, while the image processor analyzes and processes this data.
The camera captures visual information, and the illumination device provides optimal lighting for image clarity.
The image display offers visual feedback for system operators, while the mechanism and control system allow for precise movement and operation.
Together, these components form the foundation of machine vision systems, enabling the efficient capture, analysis, and interpretation of visual data.
Industrial Applications of Machine Vision
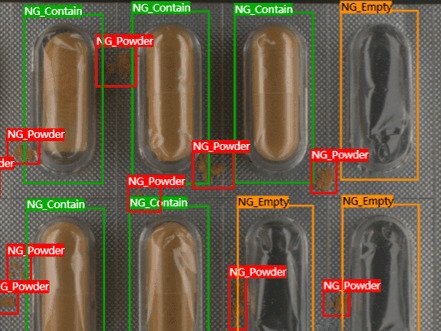
Quality Control
Machine vision automates quality control by detecting defects, surface flaws, and dimensional inconsistencies in products. It can quickly identify issues like foreign objects or imperfections, ensuring only compliant products are processed and classified.

Component Inspection
During manufacturing, machine vision inspects the assembly and positioning of components. Using image matching and measurement techniques, it ensures components are correctly installed and accurately positioned, maintaining product consistency and quality.
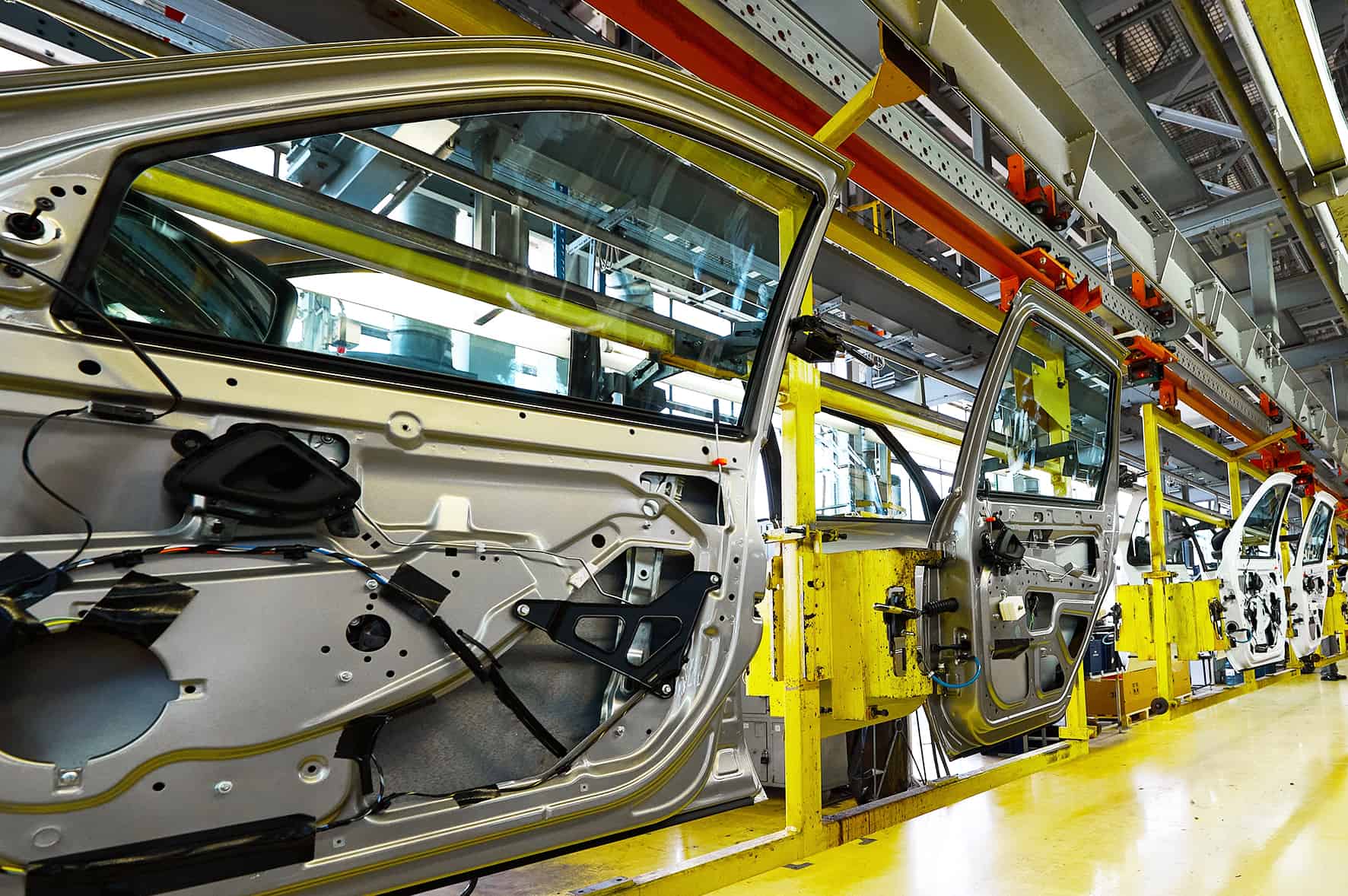

Automated Assembly
Machine vision guides robots and automated systems in assembly tasks by identifying and locating components. This enhances assembly speed and precision while reducing the need for manual labor.
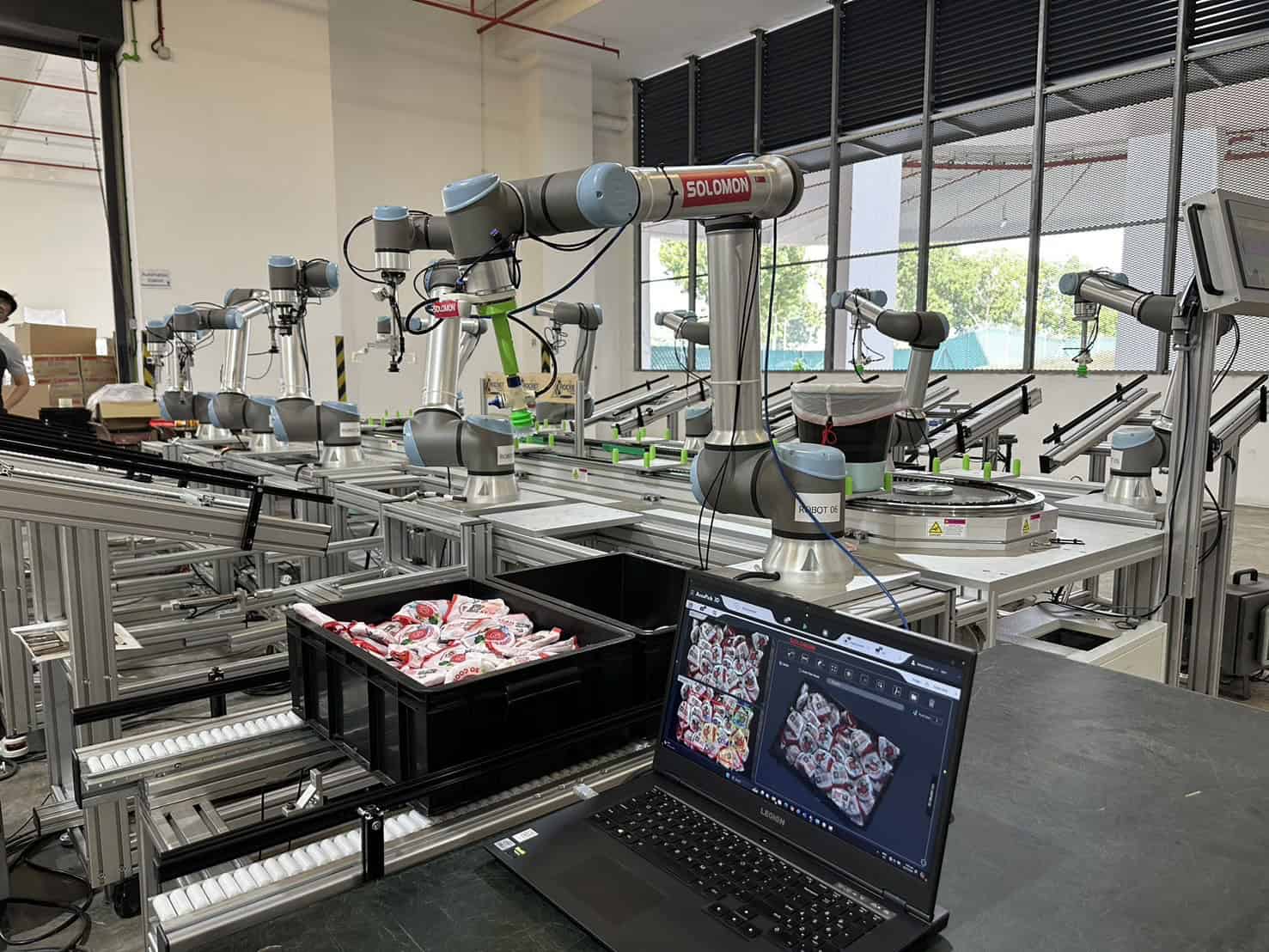

Robot Navigation
Machine vision enables robots to navigate and position themselves accurately in complex environments. By analyzing visual data, machine vision enables robots to detect obstacles and move safely while performing material handling tasks like bin picking and depalletizing.
Benefits of Machine Vision
Improved Production Efficiency and Quality
Fast, accurate, and consistent defect detection minimizes errors and reduces waste. Machine vision ensures higher product quality while increasing production speed and throughput.
Real-Time Monitoring and Feedback
Continuous monitoring of key production parameters helps detect issues early. Immediate feedback enables quick corrective actions, ensuring smooth operations and reducing downtime.
Reduced Labor Costs
Automating visual inspection reduces reliance on manual labor, cutting costs and allowing employees to focus on more skilled tasks. This improves workforce efficiency and resource allocation.
Data-Driven Optimization
Machine vision systems generate valuable insights from image data, helping manufacturers refine processes, improve quality control, and optimize production performance over time.
6 Key Trends in Machine Vision
1. Integration with Robotics and Automation
2. Edge Computing and Embedded Vision
3. Deep Learning and AI
4. 3D Vision and Depth Sensing
5. Human-Machine Collaboration
6. Augmented Reality (AR) Applications
Machine Vision Summary
